Clinical Trial Management System: The Ultimate Guide to Optimizing Trials
Feb 4, 2024
Share the article
Introduction
Modern clinical trials are more complex than ever, involving multiple sites, vast amounts of data, and strict regulatory requirements. A Clinical Trial Management System (CTMS) is a specialized software designed to handle the operational, financial, and documentation aspects of clinical research. By providing a centralized dashboard for scheduling, budgeting, and data tracking, a CTMS serves as the backbone of efficient and transparent clinical trial operations.
In the past, many research teams relied on spreadsheets and manual processes, which often led to errors, delays, and compliance risks. As trials have grown in complexity, the adoption of CTMS solutions has surged, especially with the rise of decentralized and virtual trials that demand greater flexibility and real-time collaboration. By automating key tasks and integrating seamlessly with emerging trial designs, CTMS helps researchers adapt to evolving industry demands.
A major advantage of a CTMS lies in its ability to streamline data management, bolster regulatory compliance, and foster better collaboration among sponsors, Contract Research Organizations (CROs), and research sites. It also works in tandem with Electronic Data Capture (EDC) systems and the electronic Trial Master File (eTMF) to further enhance workflow efficiency and documentation integrity.
In the following sections, we’ll dive deeper into CTMS features, benefits, and best practices to help you make informed decisions about managing clinical trials effectively.
What is a Clinical Trial Management System (CTMS)?
A Clinical Trial Management System (CTMS) is a software solution designed to streamline and enhance the efficiency of clinical trial processes. It serves as a centralized platform for managing various aspects of clinical research, from study planning to execution and reporting.
The Role of CTMS in Clinical Research
Clinical trials are complex, involving multiple stakeholders, strict regulatory requirements, and vast amounts of clinical data. A CTMS software provides a structured framework to facilitate research activities by integrating essential functions into a single platform. It acts as a project management tool tailored specifically for clinical trials, ensuring smooth collaboration between research teams, sponsors, investigators, and regulatory bodies.
Key Functions of a CTMS
A clinical trial software is more than just a database—it is a comprehensive research management system that supports:
Trial Planning & Setup – Organizing trial protocols, timelines, and objectives.
Site & Investigator Management – Tracking research sites, investigators, and their activities.
Participant Management – Monitoring enrollment, retention, and compliance of study participants.
Scheduling & Workflow Automation – Managing study schedules, visits, and milestones.
Regulatory Compliance & Document Management – Ensuring adherence to guidelines such as FDA, EMA, ICH-GCP, while storing critical documents in a structured manner.
Financial Tracking & Budgeting – Managing costs, invoicing, and financial transactions related to the trial.
Monitoring & Reporting – Real-time tracking of study progress, deviations, and insights for decision-making.
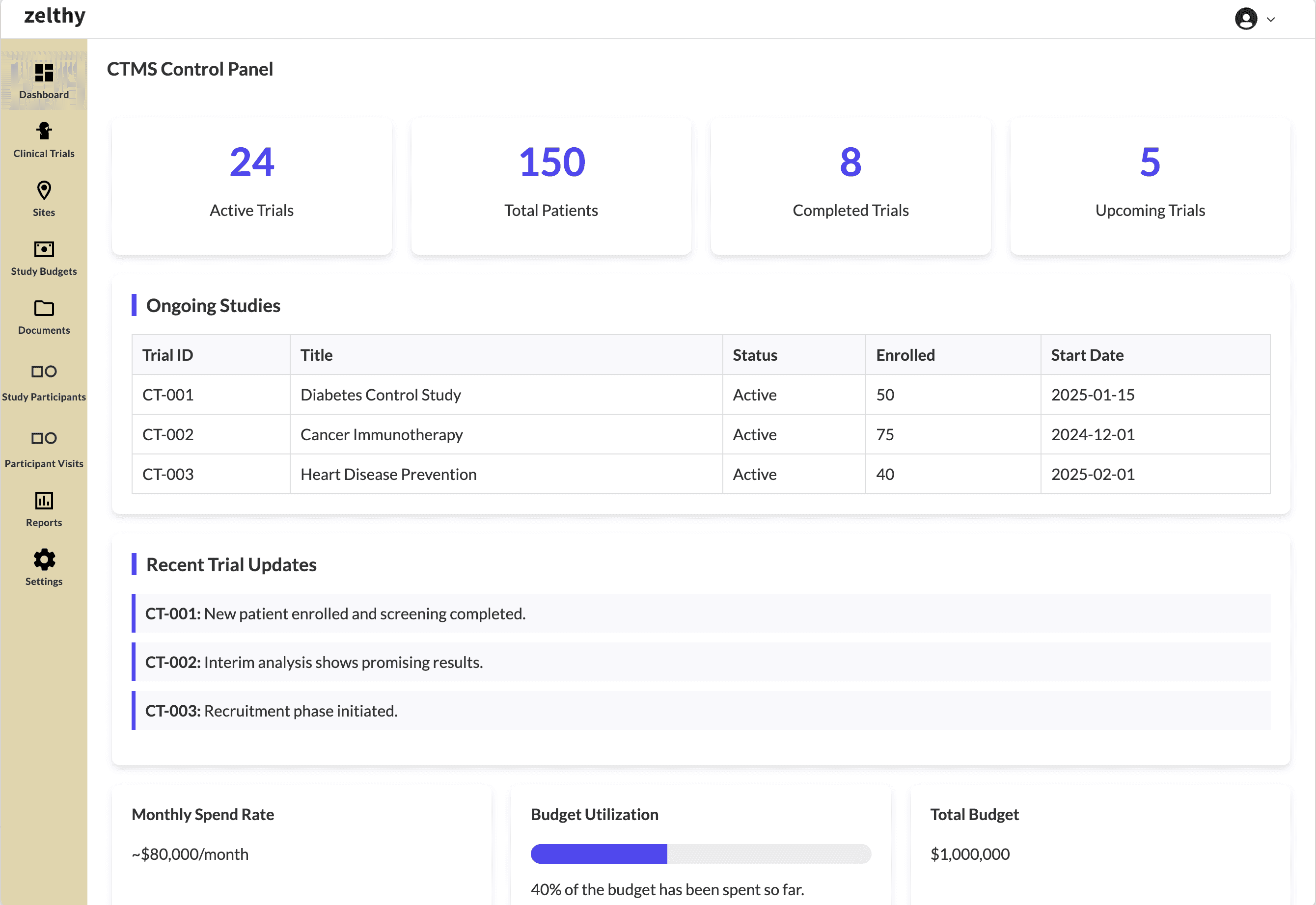
The control panel dashboard provides a consolidated view of all critical data
By integrating these functions, a CTMS can harness some core advantages ⎯
Enhanced User Experience: A CTMS unifies all trial operations into one intuitive interface, reducing the need for multiple disconnected tools.
Better Decision-Making: By offering advanced reporting and dashboards, teams gain real-time insights, fostering better decision-making throughout the study lifecycle.
Flexible Workflows: Configurable modules and workflows provide more flexibility, whether managing a single-site pilot or coordinating global, multi-center trials.
Productivity: Automated scheduling, budget tracking, and compliance checks free up valuable staff time, driving better productivity and more streamlined processes.
Robust Security Measures: Built-in encryption, role-based access, and audit trails ensure data integrity and protect sensitive patient information at every stage.
In essence, a CTMS serves as the backbone of modern clinical research, offering an all-in-one platform to manage trials efficiently while ensuring compliance and data integrity.
Why is a CTMS Important?
Clinical trials are essential for medical innovation, yet they are fraught with challenges—regulatory mandates, data management complexities, financial oversight, and patient recruitment hurdles. Without a structured approach, clinical trials can suffer from inefficiencies, delays, and compliance risks. This is where a Clinical Trial Management System (CTMS) becomes indispensable.
Addressing Key Challenges in Clinical Research
Regulatory Compliance & Ethical Standards
Regulatory bodies such as the FDA, EMA, and ICH-GCP impose strict guidelines to ensure patient safety and data integrity. A CTMS helps maintain adherence to these regulatory mandates by standardizing documentation, audit trails, and approvals, ensuring trials are conducted safely and ethically.
Data Accuracy & Centralized Management
With vast amounts of clinical trial data generated across multiple sites, maintaining accuracy is a major challenge. A CTMS acts as a centralized data management system, reducing errors and enabling real-time access to trial information, ensuring transparency and reliability.
Operational Efficiency & Streamlined Processes
Managing multiple stakeholders—including investigators, sponsors, and research teams—requires seamless coordination. A CTMS enhances collaboration and workflow automation, eliminating manual redundancies and streamlining processes for improved trial efficiency.
Financial & Resource Management
Clinical trials involve substantial investments. A CTMS helps track budgets, expenses, invoicing, and resource allocation, ensuring optimal financial planning and cost control.
The Growing Market for CTMS
As the demand for faster and more efficient clinical trials increases, the CTMS market is experiencing significant growth. Pharmaceutical companies, contract research organizations (CROs), and research institutions recognize CTMS as a crucial investment to accelerate drug development while maintaining compliance and efficiency.
By integrating critical components into a single, scalable platform, a CTMS ensures that clinical trials are accurate, compliant, and well-coordinated, ultimately contributing to advancing medical research and patient care.
Key Benefits of a Clinical Trial Management System
A Clinical Trial Management System (CTMS) is more than just software—it is a strategic tool that transforms the way clinical trials are conducted. By centralizing data, automating workflows, and ensuring regulatory compliance, a CTMS enhances efficiency, collaboration, and decision-making. Below are the key benefits of implementing a CTMS:
1. Improved Efficiency
A CTMS streamlines workflows by automating repetitive tasks, such as data capture, site management, scheduling, and reporting. Instead of relying on spreadsheets and manual tracking, research teams can manage trial operations through a structured and automated system, reducing administrative burden and saving valuable time.
2. Enhanced Collaboration
Clinical trials involve multiple stakeholders—sponsors, investigators, research coordinators, regulatory bodies, and patients. A CTMS provides a centralized platform where all participants can access real-time trial data, share documents, track progress, and communicate effectively. This fosters team synergy and ensures alignment throughout the study.
3. Reduced Errors and Data Accuracy
Manual data entry is prone to errors, which can lead to inconsistent trial results and compliance risks. A CTMS minimizes data entry mistakes by providing structured data fields, validation checks, and automated reporting tools. This ensures data accuracy and integrity, preventing costly errors and reducing the need for manual corrections.
4. Boosted Regulatory Compliance
Regulatory requirements for clinical trials are stringent, with governing bodies such as the FDA, EMA, and ICH-GCP demanding meticulous documentation and audit trails. A CTMS ensures compliance by:
Managing and storing essential regulatory documents
Tracking approvals, informed consent, and protocol adherence
Generating audit-ready reports to demonstrate regulatory compliance
By maintaining comprehensive study governance, CTMS helps research teams avoid compliance violations and regulatory penalties.
5. Improved Data Quality
Accurate and consistent data is crucial for clinical research integrity. A CTMS standardizes data collection processes, ensuring that all study sites follow the same protocols. With built-in validation checks, CTMS improves data transparency, making sure the trial results are reliable and reproducible.
6. Cost Savings
Clinical trials involve significant financial investments, and manual inefficiencies can lead to unnecessary expenses. A CTMS reduces costs by:
Eliminating paper-based processes and travel expenses
Reducing administrative overhead through workflow automation
Optimizing financial management, including budget tracking and invoicing
By streamlining operations, a CTMS maximizes cost efficiency, allowing sponsors to allocate resources effectively.
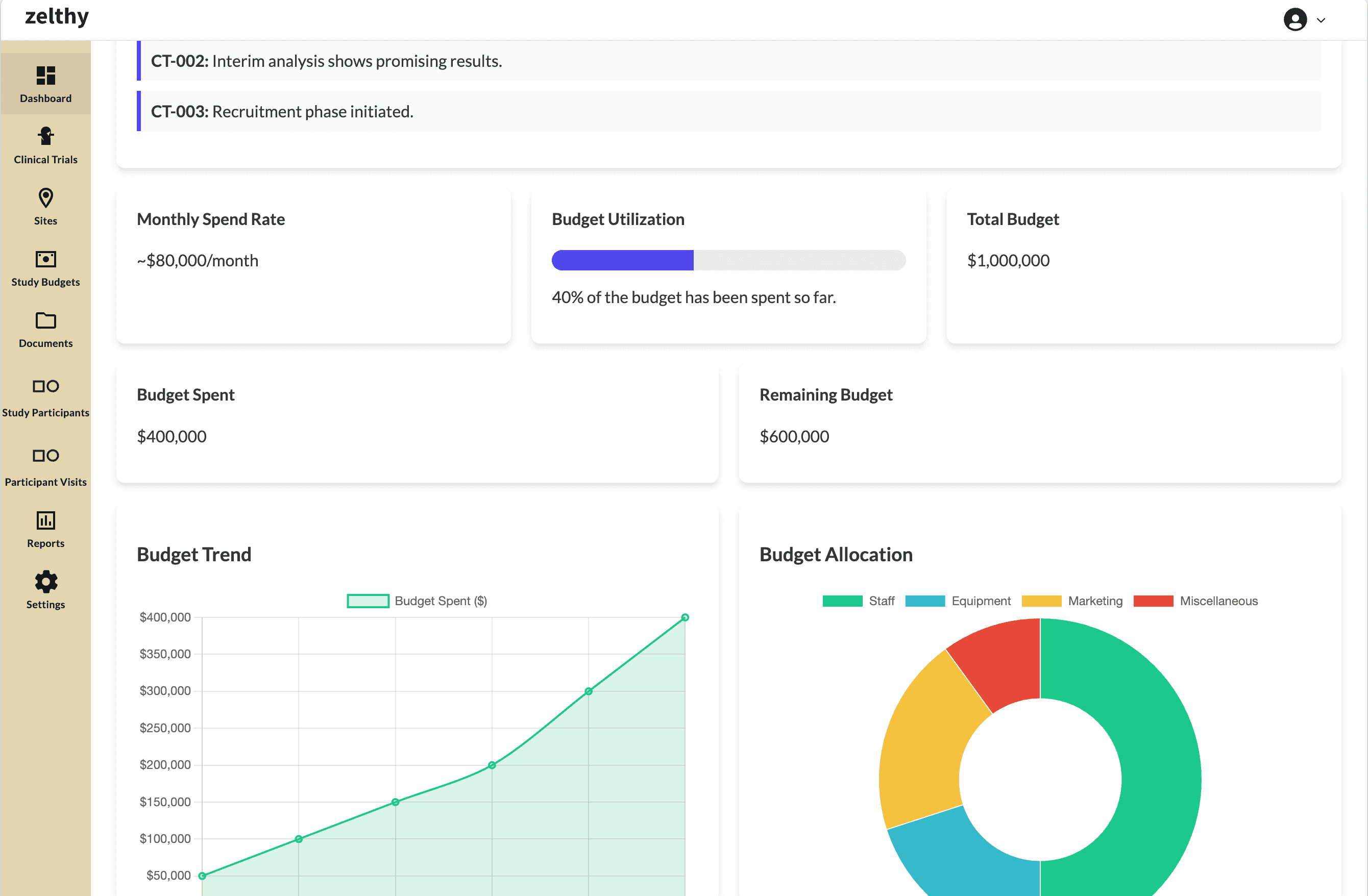
Accurately track your budget and resource utilization
7. Faster Trial Execution
Speed is a critical factor in clinical trials, as delays can impact drug development timelines and patient outcomes. A CTMS accelerates trial execution by:
Automating patient recruitment and scheduling
Tracking milestones and sending automated reminders
Facilitating quicker data collection and analysis
This results in faster study completion, allowing life-saving treatments to reach the market sooner.
8. Better Oversight & Study Governance
A CTMS provides real-time insights into trial progress, offering research teams, sponsors, and regulators a comprehensive view of study performance. With real-time dashboards and advanced reporting, organizations gain better oversight of:
Study milestones and compliance metrics
Investigator performance and site productivity
Risk assessment and issue resolution
This data-driven approach ensures proactive study management, minimizing risks and enhancing decision-making.
9. Resource Optimization
Managing resources effectively is essential for running cost-efficient and successful clinical trials. A CTMS optimizes resource allocation by:
Balancing workloads across research teams
Tracking inventory and supplies at study sites
Improving staff utilization based on trial demands
With better resource planning, organizations can avoid bottlenecks and inefficiencies, ensuring smooth trial operations.
10. Data Transparency & Real-Time Access
A CTMS centralizes all clinical trial data into one unified system, enabling seamless access to updated information. This data transparency ensures that all stakeholders—whether they are sponsors, researchers, or regulatory bodies—have access to accurate, real-time insights.
A Clinical Trial Management System is no longer a luxury—it is a necessity for modern clinical research. By enhancing collaboration, ensuring compliance, improving data management, and optimizing resources, a CTMS empowers organizations to conduct trials more efficiently, cost-effectively, and ethically. As the demand for faster and more transparent clinical trials continues to grow, investing in a CTMS is a strategic move that ensures long-term success in the evolving landscape of clinical research.
Core Features of a Clinical Trial Management System
A Clinical Trial Management System (CTMS) is a powerful tool that integrates multiple functionalities to enhance study planning, data collection, patient management, compliance, and financial oversight. It ensures clinical trials are efficient, compliant, and well-organized. Below are the core features that make CTMS an essential platform for modern clinical research.

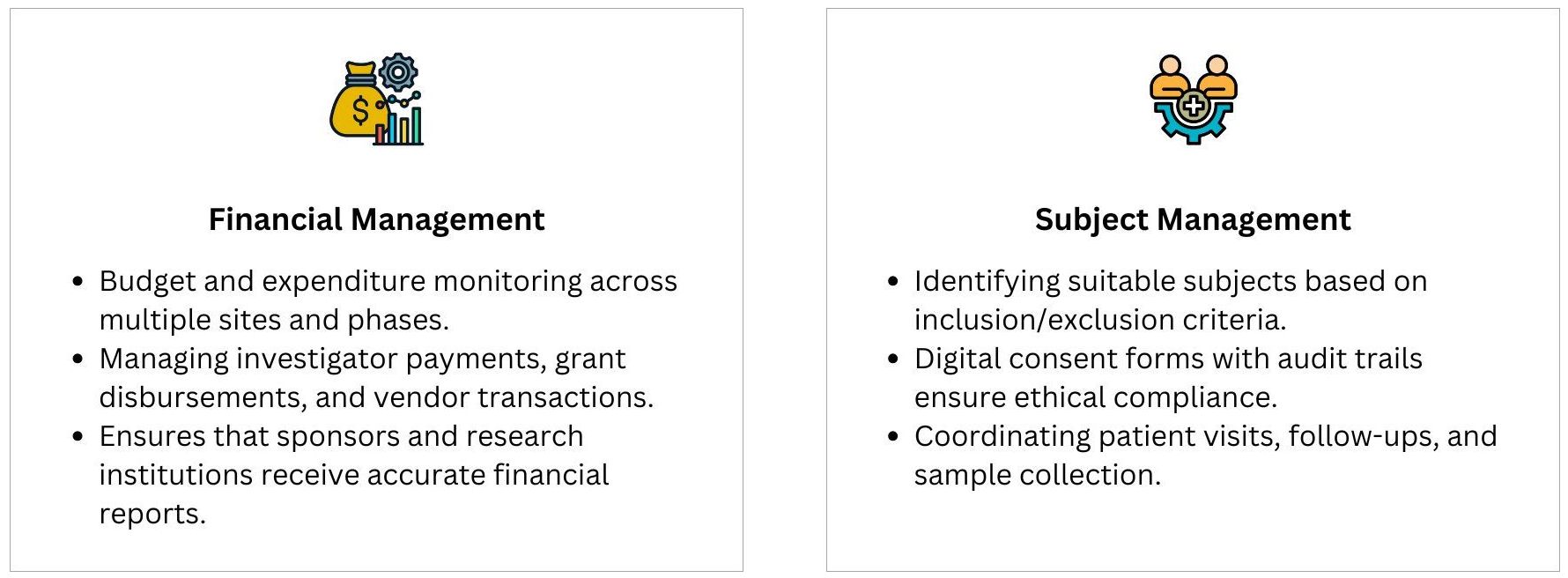

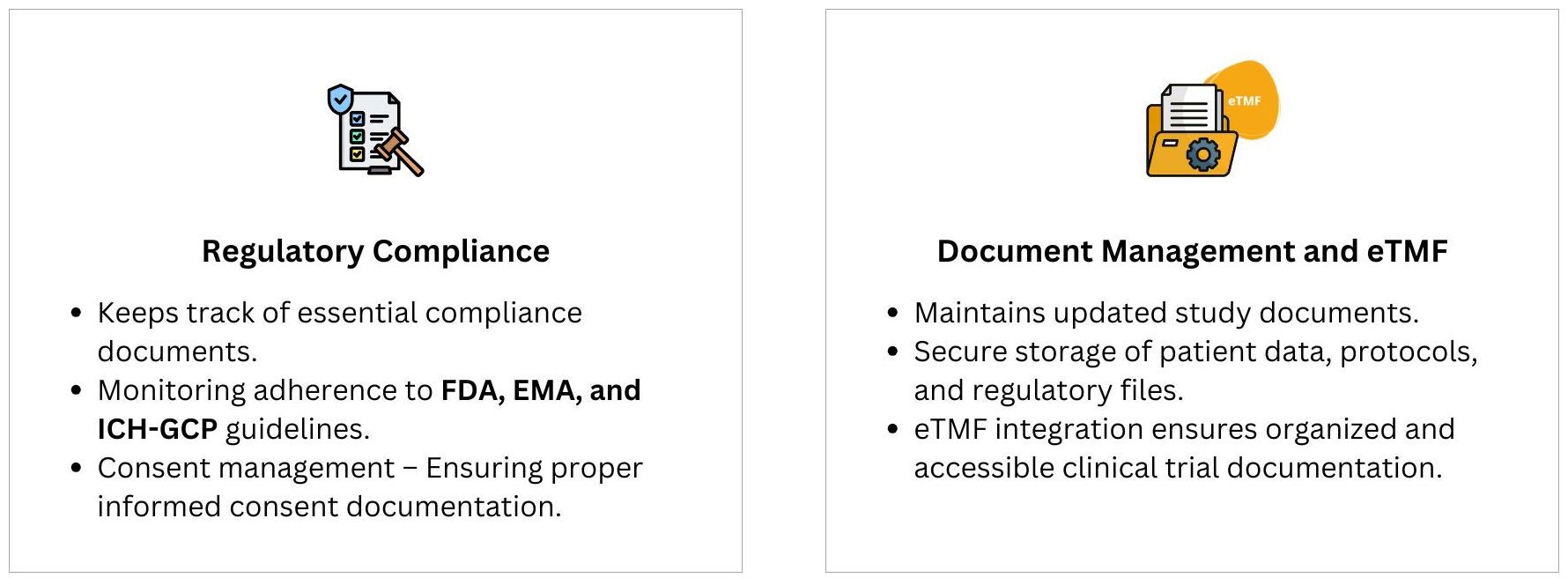
A Clinical Trial Management System is an indispensable tool that brings together all essential trial components—study planning, project management, compliance, data management, financial oversight, and patient engagement. By implementing a CTMS, research organizations can enhance efficiency, reduce errors, ensure compliance, and accelerate clinical trial success.
With the increasing complexity of clinical research, investing in a robust CTMS is no longer optional—it is a necessity for organizations aiming to deliver faster, safer, and more effective clinical trials.
How to Choose the Right Clinical Trial Management System (CTMS)
Selecting the right Clinical Trial Management System (CTMS) is a critical decision that impacts trial efficiency, regulatory compliance, and overall research outcomes. With various CTMS solutions available, organizations must evaluate their options based on customizability, usability, security, interoperability, and cost-effectiveness. Below are the key CTMS selection criteria to guide your decision.
1. Define Your Needs
Before evaluating different CTMS vendors, clearly outline your organization's specific trial management needs. Consider:
The size and complexity of your clinical trials.
The number of sites and stakeholders involved.
The need for multi-site collaboration and remote access.
Required features such as automated reporting, financial tracking, and regulatory compliance tools.
By identifying these core requirements, you can shortlist CTMS solutions that align with your research goals.
2. End-to-End Capabilities: Covering the Entire Clinical Trial Lifecycle
A robust CTMS platform should offer end-to-end capabilities, covering every stage of the clinical trial lifecycle, including:
Study Planning & Protocol Management → Automating trial design and documentation.
Patient Recruitment & Site Management → Identifying eligible patients and managing multiple trial sites.
Trial Monitoring & Risk-Based Monitoring (RBM) → Ensuring data integrity and compliance.
Data Management & Electronic Data Capture (EDC) → Seamless integration with EHR and LIMS for real-time data tracking.
Regulatory Reporting & Final Trial Submission → Generating reports for regulatory agencies like the FDA and EMA.
3. Customizability: Tailor the CTMS to Your Needs
Not all trials operate the same way, making customizability a key factor in CTMS selection. Look for:
Configurable dashboards – Customize workflows, user permissions, and reporting.
Automated workflows – Set up rule-based alerts, task automation, and site-specific configurations.
Flexible reporting tools – Generate customized trial reports tailored to sponsor, regulatory, and site-specific needs.
A highly customizable CTMS allows organizations to adapt as trials evolve, improving efficiency and compliance.
4. User Experience and Flexibility
A user-friendly CTMS significantly impacts trial efficiency. Many clinical researchers and trial coordinators are not tech experts, so an intuitive CTMS should include:
Easy navigation – Clear menus, dashboards, and search functions.
Minimal learning curve – Requires little technical expertise for trial teams.
Role-based access – Customizable user roles to streamline workflow access.
Training & Support – Providing comprehensive onboarding and training modules.
A complex system with steep learning curves can slow down clinical trials, so prioritize usability during vendor demonstrations.
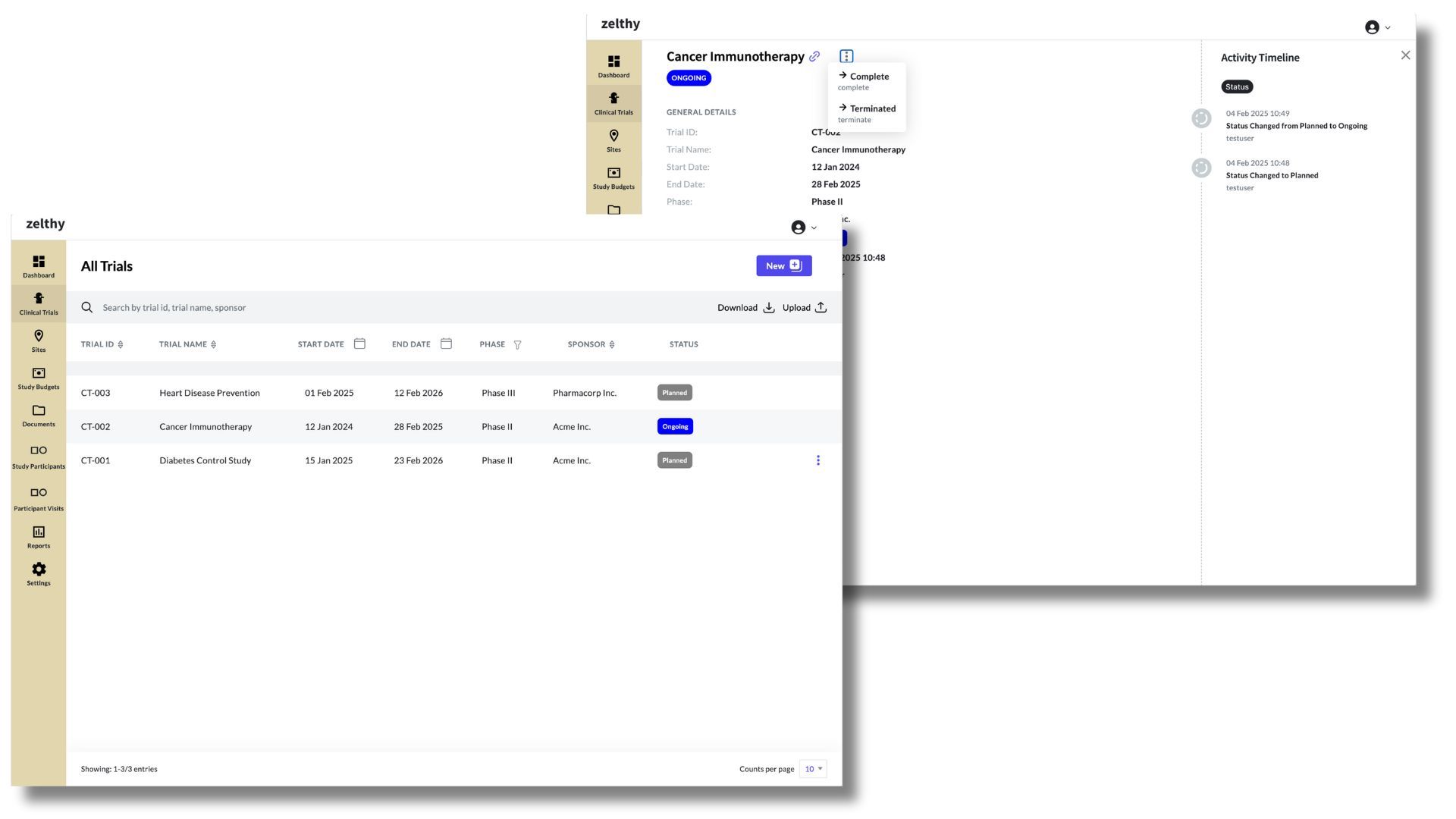
Get an overview of all ongoing trials through the clinical trials tab
5. Accessibility: Web-Based & Cloud-Enabled Solutions
A cloud-based CTMS allows research teams to access the system from anywhere, at any time. Benefits include:
Remote access – Allows sponsors, CROs, and site staff to collaborate in real time.
Reduced IT overhead – Eliminates the need for on-premise hardware and maintenance.
Automatic updates – Ensures access to the latest compliance features and security patches.
A web-based, cloud-enabled CTMS ensures seamless multi-site collaboration without geographical restrictions.
6. Interoperability: Seamless Integration with Other Systems
Modern clinical trial ecosystems rely on multiple technologies, making CTMS interoperability a top priority. A CTMS platform should seamlessly integrate with:
Electronic Trial Master File (eTMF) – Centralized document management.
Electronic Data Capture (EDC) Systems – Real-time clinical data collection.
Electronic Health Records (EHRs) → Enabling direct access to patient medical histories for eligibility screening.
Laboratory Information Management Systems (LIMS) → Automating lab result tracking and reporting.
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) & Financial Systems – Budgeting and payment processing.
CTMS interoperability eliminates data silos, improving accuracy and efficiency in clinical trial operations.
7. Value for Money: Balancing Features & Cost
Not all CTMS platforms offer the same level of functionality at similar price points. When comparing options, evaluate:
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) – Includes licensing, implementation, training, and ongoing support.
Feature-to-cost ratio – Ensure the CTMS meets essential needs without unnecessary expenses.
Pricing Model – Some vendors offer subscription-based (SaaS) or one-time license options.
A cost-effective CTMS balances functionality, compliance, and ease of use within budget constraints.
8. Scalability: Future-Proofing Your CTMS
As clinical research grows in complexity, your CTMS must scale accordingly. Look for:
Multi-site support – Can the system handle multiple studies and global trials?
Expandable data storage – Can it accommodate growing volumes of trial data?
Modular add-ons – Can you enhance capabilities as trial needs evolve?
A scalable CTMS prevents disruptions and eliminates the need for frequent system migrations.
9. Compliance: Meeting Regulatory Requirements
Ensuring regulatory compliance is a non-negotiable aspect of CTMS selection. Verify that the system:
✔️ Supports global compliance standards, including:

A CTMS that meets compliance requirements ensures audit readiness and reduces legal risks.
10. Vendor Support: Ongoing Assistance & Maintenance
Reliable vendor support is crucial for long-term CTMS success. Evaluate:
24/7 technical assistance – Availability for troubleshooting and issue resolution.
Training & onboarding programs – Ensures fast adoption among research teams.
Regular system updates – Ensures compliance with evolving regulations.
A strong vendor partnership enhances system usability and prevents downtime during critical trials.
11. Data Security: Protecting Sensitive Clinical Data
Clinical trials involve highly confidential patient and research data, making data security a top priority. Look for:
End-to-end encryption – Ensures secure data transmission.
Role-based access control (RBAC) – Restricts unauthorized data access.
Automated backups – Prevents data loss in case of system failures.
Disaster recovery plans – Ensures quick recovery from cyber threats.
A secure CTMS ensures compliance with data protection laws and safeguards trial integrity.
12. Mobile Accessibility: Enabling Remote Access
A mobile-friendly CTMS enhances accessibility for investigators, coordinators, and sponsors. Features to consider:
Mobile app availability – Enables on-the-go access to trial data.
Push notifications & alerts – Provides real-time updates on site activities.
Secure mobile login – Ensures data protection on mobile devices.
With mobile access, research teams can monitor trials remotely, improving efficiency and responsiveness.
13. Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Understanding Long-Term Investment
Beyond initial pricing, evaluate the full CTMS cost over time. Consider:
Implementation costs – Customization, data migration, and integration expenses.
Training & onboarding – Cost of training staff and system administrators.
Maintenance & updates – Regular system upgrades and vendor support fees.
By assessing the total cost of ownership, organizations can make informed, long-term investments.
Choosing the right CTMS requires a comprehensive evaluation of features, scalability, security, and cost-effectiveness. By prioritizing usability, interoperability, compliance, and vendor support, organizations can select a CTMS that enhances efficiency, reduces trial risks, and ensures regulatory adherence.
A well-chosen CTMS not only streamlines operations but also future-proofs clinical research, enabling faster and more accurate trial execution.
CTMS Implementation
Implementing a Clinical Trial Management System (CTMS) is a critical step in optimizing clinical trial processes, ensuring data accuracy, and maintaining regulatory compliance. A well-planned CTMS implementation enhances efficiency and streamlines workflows. Below is a structured implementation plan to ensure a successful deployment.
1. Form a Cross-Functional Team
A CTMS implementation requires collaboration across multiple departments. Creating a cross-functional team ensures that all stakeholders are aligned from the beginning. The team should include:
Clinical Operations – Ensures the CTMS meets research workflow needs.
IT & Data Management – Manages system configuration, integration, and security.
Regulatory & Compliance Officers – Ensures adherence to FDA, EMA, and ICH-GCP guidelines.
Finance & Budgeting Teams – Monitors trial expenses and financial management.
End Users (Investigators, Coordinators, and Sponsors) – Ensures usability and adoption.
This approach provides comprehensive oversight, ensuring that the CTMS aligns with organizational goals.
2. Develop a Clear Implementation Plan
A structured CTMS implementation plan helps prevent delays, miscommunication, and budget overruns. Key components include:
Defining Objectives – What problems will the CTMS solve?
Establishing Timelines – Setting realistic deployment deadlines.
Budget Planning – Allocating resources for system implementation, training, and support.
Identifying Responsibilities – Assigning roles to team members.
A detailed roadmap ensures a smooth transition from legacy systems to a modern CTMS solution.
3. Select a CTMS Vendor
Choosing the right CTMS vendor is crucial for long-term success. Factors to consider when selecting a vendor include:
Scalability & Customization – Can the CTMS adapt to future study needs?
User-Friendliness – Is the system intuitive and easy to navigate?
Integration Capabilities – Can it integrate with eTMF, EDC, and other trial management tools?
Regulatory Compliance – Does it support FDA 21 CFR Part 11, ICH-GCP, and GDPR compliance?
Customer Support & Maintenance – Is there ongoing support available?
A thorough vendor evaluation ensures you invest in a CTMS that meets your organization’s requirements.
4. Configure and Customize the CTMS
Once a vendor is selected, the system needs to be configured and customized to align with your organization’s workflows. Key steps include:
Defining User Roles & Access Levels – Ensuring secure access based on responsibilities.
Customizing Dashboards & Reports – Tailoring insights to trial-specific needs.
Integrating with Existing Systems – Ensuring seamless connection with EHRs, eTMF, and financial tools.
Workflow Automation – Setting up automated alerts, task management, and approval processes.
This tailored configuration enhances usability and maximizes the system’s effectiveness.
Site and Subject Management Interface respectively
5. Data Migration and System Validation
Transferring historical trial data from legacy systems to a new CTMS requires meticulous planning. The process includes:
Data Extraction & Cleaning – Identifying and eliminating redundant or outdated data.
Secure Data Migration – Ensuring encrypted transfer of patient records, financials, and trial documents.
System Validation & Testing – Conducting user acceptance testing (UAT) to verify functionality.
Compliance Checks – Ensuring regulatory data integrity and audit readiness.
Rigorous data validation guarantees data accuracy and system reliability before full deployment.
6. User Training for Effective Adoption
A CTMS is only as effective as its users. Proper user training ensures adoption and proficiency. Training should include:
Role-Based Training – Tailoring learning modules for investigators, coordinators, and sponsors.
Hands-On Workshops – Interactive sessions to enhance system familiarity.
Simulation-Based Learning – Running test scenarios for data entry, compliance tracking, and reporting.
Training Documentation – Providing user manuals, FAQs, and online resources for continuous learning.
A well-trained team maximizes the CTMS’s potential, leading to higher efficiency and fewer errors.
7. Ongoing Support and System Maintenance
Implementation doesn’t end with deployment—ongoing support ensures long-term success. Key post-implementation actions include:
Monitoring System Performance – Identifying and addressing system issues.
Regular Updates & Enhancements – Keeping the CTMS compliant with evolving regulations.
User Feedback & Continuous Training – Refining workflows based on end-user insights.
Vendor Support & Troubleshooting – Ensuring 24/7 assistance for system-related concerns.
By investing in continuous support and optimization, organizations can maximize the benefits of their CTMS.
A successful CTMS implementation requires a structured approach—from selecting the right vendor to training users and ensuring ongoing support. By following a clear implementation plan, clinical trial teams can:
Enhance trial efficiency
Ensure regulatory compliance
Optimize data management
Improve collaboration among stakeholders
With proper planning and execution, a CTMS can revolutionize clinical trial operations, leading to faster, more cost-effective, and compliant research.
Emerging Trends and Technologies in CTMS
The clinical research landscape is evolving at a rapid pace, and Clinical Trial Management Systems (CTMS) are at the forefront of this transformation. Innovations such as AI, machine learning, and blockchain are reshaping how trials are conducted, managed, and monitored. Below are key trends and technologies that are influencing the future of CTMS:
1. AI and Machine Learning
Advancements in AI and machine learning help automate repetitive tasks like data entry and validation, reducing errors and saving time. By analyzing large datasets, these technologies can optimize patient selection and predict outcomes, making it easier to identify suitable trial participants. Furthermore, ML algorithms support adaptive trials by quickly adjusting study parameters based on evolving data, ultimately speeding up the decision-making process.
2. Decentralized Trials
A shift toward decentralized clinical trials means more remote monitoring and virtual patient interactions. CTMS platforms are adapting to this model by integrating telemedicine, home health visits, and mobile apps for collecting patient data. This approach reduces the need for frequent in-person visits, improving patient engagement and expanding trial access to participants who may live far from research sites.
3. Cloud-Based Solutions
Moving CTMS to the cloud enables real-time data access, promotes remote collaboration, and lowers infrastructure costs. With cloud-based CTMS, research teams, sponsors, and regulatory bodies can securely log in from anywhere, anytime. This flexibility also streamlines system maintenance, as updates and patches are handled centrally, ensuring users always have access to the latest features and security enhancements.
4. Patient-Centric Solutions
Clinical trials are increasingly focusing on patient-centric solutions. Modern CTMS platforms provide user-friendly portals and mobile applications that guide participants through each step of the study. These interfaces often include appointment reminders, educational materials, and direct messaging features for easy communication. Such patient-focused enhancements boost retention and make trials more inclusive.
5. Blockchain Technology
Blockchain is emerging as a tool for securing sensitive healthcare data. In the context of CTMS, blockchain can provide a tamper-resistant record of trial activities, helping track consent forms, protocol changes, and data transfers. This added layer of security reduces the risk of data breaches and fosters trust among participants, sponsors, and regulatory authorities.
6. EHR Integration
Integrating electronic health records (EHR) with a CTMS promotes seamless data exchange, reducing manual data entry and potential errors. Researchers can pull patient information directly from healthcare databases, leading to more accurate analyses and faster patient recruitment. This connectivity also simplifies post-trial follow-up and safety monitoring.
7. Mobile Apps and Wearables
The use of mobile applications and wearable devices is transforming data collection by capturing real-time information about patient health, activity levels, and adherence to study protocols. Data can be automatically synced to the CTMS, giving researchers immediate insights and reducing the burden on participants to maintain detailed logs.
8. Telemedicine and Virtual Trials
Telemedicine solutions allow investigators to conduct remote consultations, reducing travel time for both patients and staff. Virtual trial visits can include electronic data capture and digital consent, further streamlining study workflows and broadening the participant pool.
From AI-driven insights to decentralized approaches and patient-centric solutions, the future of CTMS is focused on efficiency, security, and improved participant experiences. By embracing these emerging trends, clinical research teams can conduct trials that are faster, more inclusive, and better aligned with the evolving needs of modern healthcare.
CTMS vs. Other Systems: A Comparative Overview
Clinical Trial Management Systems (CTMS) play a pivotal role in coordinating and overseeing the many moving parts of a clinical study. However, other platforms—such as Electronic Data Capture (EDC) systems, spreadsheet tools like Excel, and Electronic Trial Master File (eTMF) solutions—also hold significance in clinical research. Below is a closer look at how each compares to a CTMS.
CTMS vs. EDC
While both a CTMS and an EDC system manage aspects of clinical research, their core functions differ:
CTMS focuses on operational efficiency—scheduling visits, tracking budgets, assigning tasks, and providing overall trial oversight.
EDC, on the other hand, is primarily used for electronic data capture: collecting, validating, and cleaning patient data during a study.
A robust clinical research environment often integrates both systems. The CTMS can automate study workflows and financial management, while the EDC handles patient-specific data entry, ensuring accurate data for statistical analysis.
CTMS vs. Excel
Some organizations may attempt to manage clinical trials using Excel spreadsheets. While Excel can work for small-scale projects, it falls short when handling the complex workflows and regulatory requirements of large or multi-center trials. Key limitations include:
Lack of Scalability – As the trial grows, manual data entry and numerous spreadsheets become difficult to maintain.
Limited Collaboration – Sharing Excel files across teams and sites can lead to version control issues and data discrepancies.
Regulatory Compliance – Excel is not designed to meet compliance standards (e.g., audit trails, electronic signatures).
A CTMS addresses these gaps by providing centralized data, role-based access, compliance tracking, and secure audit trails.
CTMS vs. eTMF
A CTMS and an Electronic Trial Master File (eTMF) system are complementary but serve different purposes:
CTMS streamlines operational aspects (site management, milestones, financial tracking).
eTMF focuses on document management and regulatory compliance, storing study protocols, informed consent forms, and other essential trial documents.
While an eTMF can maintain document integrity and audit readiness, a CTMS ensures that every operational step—scheduling, budget, resource allocation—is organized and tracked efficiently. Many organizations integrate both systems for a complete picture of trial progress and compliance.
Comparison Table
Below is a concise comparison of CTMS, EDC, eTMF, and Excel based on some key criteria:
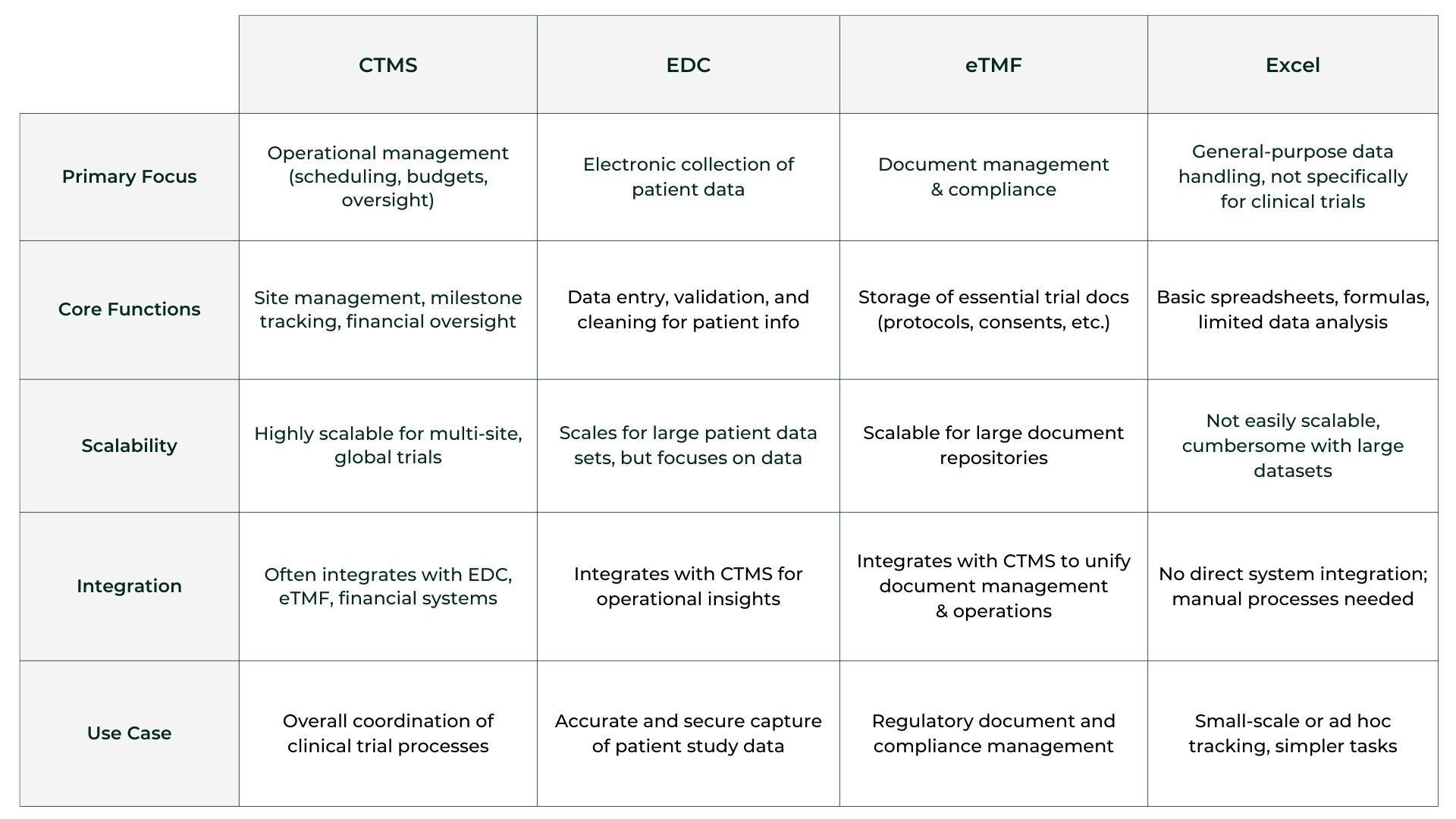
When to Use Each System
1. CTMS: Best used for tracking trial progress, managing budgets, and ensuring operational efficiency.
2. EDC: Essential for capturing and managing patient data electronically in a secure manner.
3. eTMF: Ideal for storing and maintaining regulatory documents required for compliance.
4. Excel: Used for basic data tracking and manual entry but lacks automation, compliance features, and scalability needed for clinical trials.
In summary, a CTMS drives operational success in clinical trials, an EDC focuses on accurate data capture, an eTMF secures and organizes regulatory documents, and Excel is best reserved for smaller or less complex projects. By integrating the right systems—and avoiding reliance on inadequate tools—research teams can enhance trial efficiency, reduce errors, and ensure regulatory compliance at every stage.
The Cost of a Clinical Trial Management System
Investing in a Clinical Trial Management System (CTMS) involves more than just paying for the software license. Several factors—such as software complexity, the scope of features, the number of integrations, and the size of the development team—can significantly influence overall CTMS pricing. In addition, implementation costs and subscription fees often vary depending on whether you choose an on-premise solution or a cloud-based (SaaS) model.
Cost Influencers
1. Complexity & Features: A CTMS with advanced functionalities—like real-time analytics, AI-driven insights, or sophisticated financial modules—will typically cost more than a basic system focusing on simple study management tasks.
2. Number of Integrations: If you need the CTMS to integrate with other systems (e.g., EDC, eTMF, EHR), expect higher costs for configuration and ongoing maintenance.
3. Development & Customization: Tailoring a CTMS to meet specific organizational workflows or unique regulatory requirements increases both the upfront and long-term expenses.
Implementation & Training: Costs also include data migration, user training, and technical support to ensure smooth adoption.
Typical Price Ranges
Basic CTMS
A basic CTMS typically includes essential functionalities such as study planning, site management, and monitoring. For a small to medium-sized organization, the first-year costs can range from $4,000 to $100,000. This estimate encompasses:
Setup Fees: One-time costs for system installation and initial configuration.
User Licenses: Subscription fees, often ranging from $25 to $400 per user per month.
Training and Support: Expenses for user training and ongoing technical support.
Advanced CTMS
For organizations requiring advanced features like AI-powered analytics, extensive integrations, and real-time data processing, the costs are higher. First-year expenses can range from $50,000 to over $500,000, which may includes
Customization: Tailoring the system to specific organizational needs.
Advanced Integrations: Connecting with multiple external systems, such as Electronic Data Capture (EDC) platforms and Quality Management Systems (QMS).
Regulatory Compliance: Ensuring adherence to standards like 21 CFR Part 11.
It's important to note that these figures are approximate and can vary based on the specific requirements and vendor pricing models. For instance, some vendors offer subscription plans starting at $124 per month, while others may charge $300 to $400 per user per month.
When evaluating CTMS options, consider not only the initial costs but also long-term expenses related to maintenance, updates, and scalability to ensure the system aligns with your organization's evolving needs. Ultimately, the total cost of ownership depends on how closely the system aligns with your organization’s needs, as well as the complexity of your clinical trials and regulatory environment.
Off-The-Shelf vs Custom-Builds
When choosing a clinical trial management software—often referred to as a CTMS—organizations can opt for either an off-the-shelf solution or a custom build. Both approaches serve essential functions such as data management, patient management, and regulatory compliance, yet their differences can significantly impact ROI.
Off-The-Shelf Solutions
Typically faster to implement, providing immediate access to a tested eClinical platform.
Best for smaller teams or studies that need standardized features like EDC (electronic data capture) and trial management dashboards.
May offer limited flexibility, especially as decentralized clinical trials evolve.
Custom-Builds
Designed to align with specific workflows, accommodating unique requirements like advanced reporting or seamless integrations with existing systems.
Can incorporate specialized features for decentralized clinical trials, enhancing patient management and remote monitoring.
While initial development may be more expensive, a tailored solution often delivers greater ROI over time by boosting efficiency and scalability.
Ultimately, the choice depends on your organization’s budget, timeline, and long-term objectives for robust trial management.
Given below is a comparison of some of the most popular market-available CTMS software and Zelthy’s custom-built solution.
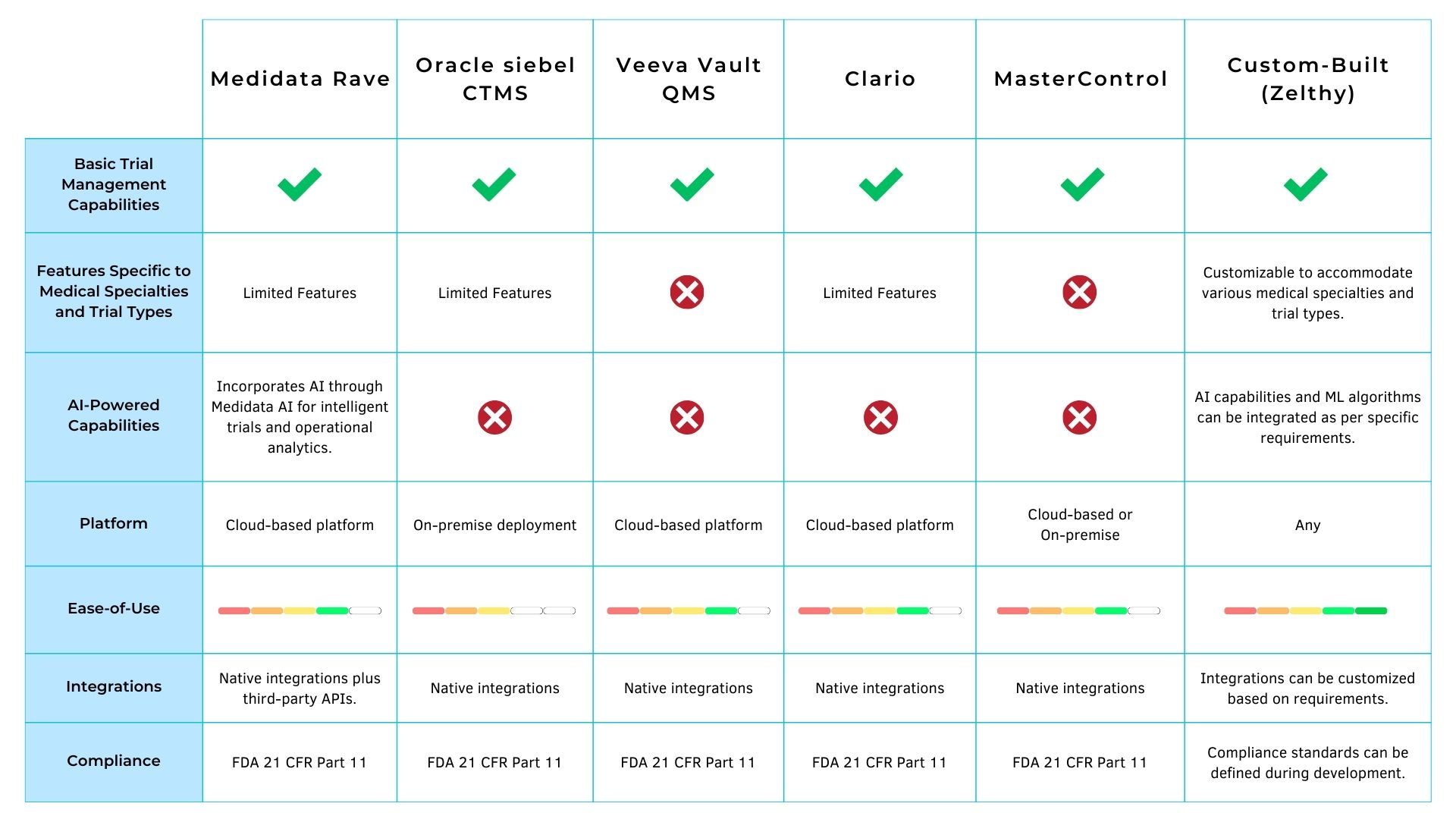
Why You Should Consider Zelthy When Building Your CTMS
Off-the-shelf Clinical Trial Management Systems (CTMS) often come with rigid workflows, expensive licensing, and limited customization. Zelthy, on the other hand, offers a tailored, scalable, and future-proof solution that eliminates inefficiencies while meeting your exact trial requirements.
Why Zelthy Stands Out
1. Custom-Built for Your Needs
Unlike standardized solutions like Medidata Rave or Clario, Zelthy is fully customizable for any trial type, specialty, or workflow.
You don’t have to adjust your processes to fit the software—Zelthy adapts to your organization’s unique needs.
2. Seamless AI and Automation
While AI is optional or expensive in other CTMS, Zelthy allows flexible AI integration for predictive enrollment, adaptive trial design, and risk-based monitoring.
Automates key workflows like study budgeting, monitoring visits, regulatory approvals, and compliance tracking.
3. Deployment Flexibility
Most CTMS solutions are either cloud-only (Veeva, Clario) or on-premises-only (Oracle Siebel CTMS).
Zelthy supports both, ensuring alignment with your IT security and compliance needs.
4. Faster Iterations and Agile Enhancements
Large enterprise CTMS solutions have slow development cycles.
Zelthy enables rapid iteration and feature updates, ensuring your system evolves with your trial demands.
5. Deep Integrations Without Vendor Lock-in
Ready-to-use APIs for seamless integration with Veeva eTMF, QMS, EDC systems, and third-party tools—without waiting on vendor roadmaps.
6. Compliance and Audit Readiness
21 CFR Part 11-compliant, with custom audit trails and e-signature workflows tailored to your specific regulatory requirements.
Supports Medicare Coverage Analysis for clinical trial billing compliance.
A Future-Proof CTMS
With Zelthy, you don’t just get a CTMS—you get a dynamic platform that grows with your research needs, offering unparalleled flexibility, compliance, and operational efficiency.
The Future of Clinical Trial Management with CTMS
As clinical research continues to evolve, Clinical Trial Management Systems (CTMS) have become indispensable for improving efficiency, accuracy, and compliance in the pharmaceutical industry. By automating critical processes, CTMS reduces administrative burden, minimizes risks, and ensures regulatory compliance at every stage of a study, allowing researchers to focus on medical innovation.
As the pharmaceutical industry continues to evolve, CTMS platforms will likely integrate emerging technologies—from AI-powered analytics to decentralized trial capabilities—further enhancing patient engagement and data quality. For organizations looking to stay competitive and bring new treatments to market efficiently, investing in a robust CTMS is no longer optional; it is a strategic move. Exploring how a CTMS can strengthen and streamline your trial processes can pave the way for more innovative, compliant, and successful clinical trials.
Frequently Asked Questions About CTMS
What is a Clinical Trial Management System (CTMS)?
A CTMS is a software platform designed to streamline and coordinate all aspects of a clinical trial. It centralizes data related to protocol management, site details, participant tracking, financials, and regulatory documents. By automating tasks like scheduling, budget tracking, and reporting, a CTMS helps researchers maintain compliance, reduce errors, and manage large volumes of information more effectively throughout the trial lifecycle.
What is the purpose of clinical trial management?
Clinical trial management ensures that each phase of a study runs smoothly, from planning and site selection to data collection and reporting. The goal is to maintain compliance with regulatory standards, manage budgets effectively, and keep all stakeholders informed. By coordinating tasks like participant enrollment, data monitoring, and documentation, trial management helps bring new treatments to market faster and more safely—ultimately improving patient care.
What can a CTMS help with?
A Clinical Trial Management System (CTMS) streamlines processes such as site management, participant tracking, scheduling visits, and financial oversight. It centralizes critical data, automates routine tasks, and generates real-time reports for better decision-making. By reducing administrative burdens and errors, a CTMS improves overall trial efficiency, boosts team collaboration, and ensures timely compliance with regulatory bodies.
Who uses CTMS?
CTMS platforms are used by a range of professionals involved in clinical research: sponsors, contract research organizations (CROs), clinical research coordinators, principal investigators, and data managers. Regulatory teams also leverage CTMS features to track compliance requirements. Essentially, any stakeholder needing centralized oversight of clinical trials relies on a CTMS for more organized and transparent management of study operations.
What is the difference between CTMS and CDMS?
A CTMS (Clinical Trial Management System) primarily handles operational activities—scheduling, budgeting, site management, and reporting. A CDMS (Clinical Data Management System) focuses on collecting, cleaning, and validating trial data. While CTMS tracks overall trial progress and logistics, the CDMS zeroes in on the integrity and accuracy of patient data. Often, organizations integrate both systems for comprehensive trial oversight and data quality.
How to manage a clinical trial?
Effective clinical trial management involves several steps:
Planning: Define objectives, timelines, and budgets.
Site Selection: Choose appropriate research locations and investigators.
Participant Management: Recruit, screen, and enroll eligible patients.
Data Collection: Capture patient data accurately and securely.
Monitoring & Compliance: Conduct regular reviews for quality assurance.
Analysis & Reporting: Evaluate results, prepare publications, and submit findings to regulatory bodies.
Using a CTMS simplifies these tasks by centralizing data and workflows.
What is the difference between EDC and CTMS?
Electronic Data Capture (EDC) systems focus on collecting patient data—such as vital signs or lab results—directly from study sites or patients. In contrast, a CTMS manages operational functions like site activation, trial scheduling, budget tracking, and communication with stakeholders. EDC ensures high-quality clinical data, while CTMS offers a broader project management perspective, coordinating all components of the trial from start to finish.
What are the tasks of CTMS?
A CTMS handles:
Site Management: Tracking site performance and investigator credentials.
Participant Oversight: Monitoring enrollment, consent forms, and visit schedules.
Financial Tracking: Managing budgets, invoices, and payments.
Document Management: Organizing essential regulatory and trial documents.
Reporting & Analytics: Generating real-time insights on study progress.
These capabilities streamline workflows and ensure trials stay on schedule, on budget, and in compliance.
Why do we need clinical data management?
Clinical data management ensures that patient information collected during a trial is accurate, reliable, and secure. High-quality data is critical for analyzing trial outcomes, obtaining regulatory approvals, and safeguarding patient well-being. By minimizing errors and inconsistencies, robust data management supports informed decision-making, speeds up the research process, and enhances the overall credibility of study findings.
Why is CTMS important in clinical trials?
A CTMS centralizes and automates many key aspects of a clinical trial, allowing teams to collaborate more effectively. It keeps track of timelines, budgets, participant information, and documentation, ensuring every detail aligns with regulatory standards. By reducing manual tasks, a CTMS also decreases the risk of errors, ultimately helping deliver accurate, timely results that can lead to new therapies and medical innovations.
What features should I look for in a CTMS?
Key features include:
Project Management: Trial scheduling, milestone tracking, and site oversight.
Financial Management: Budgeting, invoicing, and payment processing.
Regulatory Compliance: Audit trails and document control.
Data Integration: Compatibility with EDC, eTMF, and other systems.
Reporting & Analytics: Real-time dashboards for performance insights.
These capabilities help ensure efficient, compliant, and transparent trial operations.
Can CTMS integrate with other clinical trial tools?
Yes. Many CTMS platforms offer APIs and built-in connectors that allow seamless data exchange with other systems like Electronic Data Capture (EDC), eTMF (Electronic Trial Master File), or even Electronic Health Records (EHR). By integrating multiple tools, organizations reduce duplicate data entry, streamline workflows, and gain a more comprehensive view of study activities, which ultimately improves overall trial efficiency.
How do CTMS platforms ensure regulatory compliance?
Most CTMS solutions offer built-in controls—such as audit trails, electronic signatures, and permission-based access—to comply with guidelines from bodies like the FDA (21 CFR Part 11) or EMA. They track and store essential documents, maintain version histories, and log every change made to the data. This transparency and traceability help organizations easily demonstrate adherence to regulations during audits or inspections.
What are the benefits of using cloud-based CTMS solutions?
Cloud-based CTMS solutions provide:
Real-Time Accessibility: Teams can log in from anywhere, streamlining collaboration.
Reduced IT Costs: Providers handle maintenance and security updates.
Scalability: Easily add new users, sites, or studies without major infrastructure changes.
Automatic Upgrades: Stay current with the latest features and compliance standards.
These advantages make cloud-based CTMS particularly appealing for organizations aiming to grow or manage multiple studies efficiently.
What challenges do organizations face when adopting a new CTMS?
Common hurdles include:
Change Management: Getting teams to adapt to new workflows.
Data Migration: Ensuring accurate transfer of legacy data.
Integration Complexity: Linking the CTMS with existing systems.
Training & Support: Providing adequate resources for users to learn the platform.
Despite these obstacles, careful planning, stakeholder engagement, and robust vendor support can smooth the transition and maximize benefits.
How much does a CTMS cost?
Costs vary widely based on system complexity, features, and the number of integrations required. A basic, off-the-shelf solution might range from $10,000 to $40,000 per year, whereas advanced CTMS platforms with custom workflows and integration capabilities can exceed $50,000 annually. Additional expenses—such as implementation, data migration, and ongoing training—should also be factored into the total cost of ownership.
Looking for a scalable CTMS? Book a free demo with us today.
Write to us at connect@zelthy.com to learn more about our solutions and how they can enhance your healthcare efficiency. Or DM us on LinkedIn.
