Using Gitpod
About Gitpod
Gitpod is a cloud development environment (CDE) that enables you to develop your projects in a pre-configured workspace directly from your browser. With Gitpod, you can write, debug, and collaborate on your projects without the need for complex setups or installations.
Launching Gitpod workspace
To get started with using Zango in gitpod, you can click on the button below:
Please refer to the video above and follow the steps to launch the workspace and set up the Zango project.
Gitpod Workspace Terminals
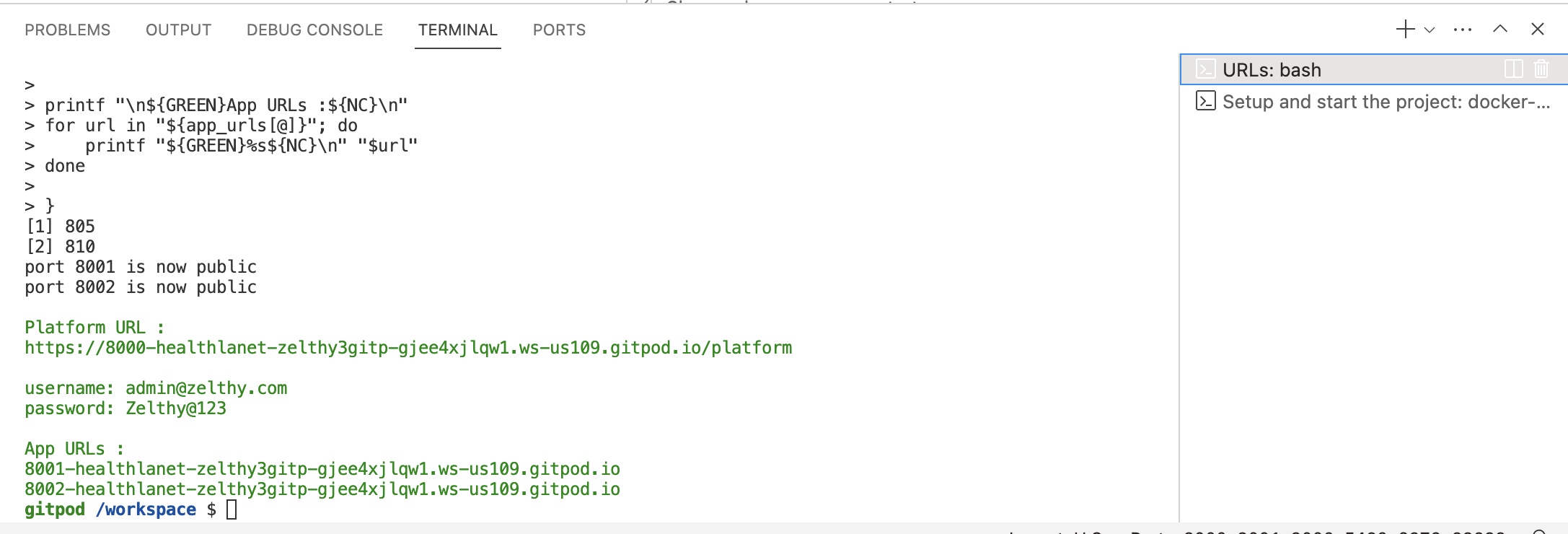
Terminal URLs
This terminal contains the available URLs that can be mapped to the apps launched in the workspace.
Terminal Setup and start the project
In this terminal, Zango Docker containers are running.
You can use the following commands to start and stop the containers.
To start the containers, run
docker-compose up
To stop the containers, run
docker-compose down
Running management commands
All the Zango services, such as the app server, database, Celery, and Redis, are running as Docker containers in the Gitpod workspace.
To run the management commands, you will need to enter the app container:
docker exec -it sandbox-app-1 bash
Once you are in the app container, you can run the management commands from the zango_project directory:
Example:
gitpod@b1be57580132:/zango/zango_project$ python manage.py ws_migrate <app_name>
Gitpod Notes
Billing
The Gitpod free plan currently allows 500 free credits per month, which is 50 hours of standard workspace usage. Usage information can be found in the Gitpod billing section
Workspace Lifecycle
You can check out the Gitpod docs on Workspace Lifecycle
“Starting” & “Stopping” workspaces
“Workplace Inactivity”: By default, workspaces stop following 30 minutes without user input (e.g. keystrokes or terminal input commands).
Workspaces are deleted after 14 days. Pinned workspaces are never deleted automatically.
You can pin a workspace from your workspace list in the Gitpod dashboard.
For more information about gitpod, visit Gitpod Docs